



 |
 |
 |
Performing fibre-tracking |  |
|---|
To illustrate the command syntax, we start with a very simple example of tensor-based fibre-tracking (see e.g. Mori & van Zijl, 2002 for a review):
> streamtrack DT_STREAM dwi.mif -seed -5.3,17,-30.7,3 -mask mask.mif cst_dt.tck
122 generated, 100 selected [100%]
This generates 100 tracks (the default) using deterministic streamlines,
with orientations calculated using the diffusion tensor model.
The tracks are seeded at random from a spherical ROI position at [ -5.3 17 -30.7 ] with a 3 mm radius.
The mask image mask.mif is also specified to terminate tracks as they leave the brain.
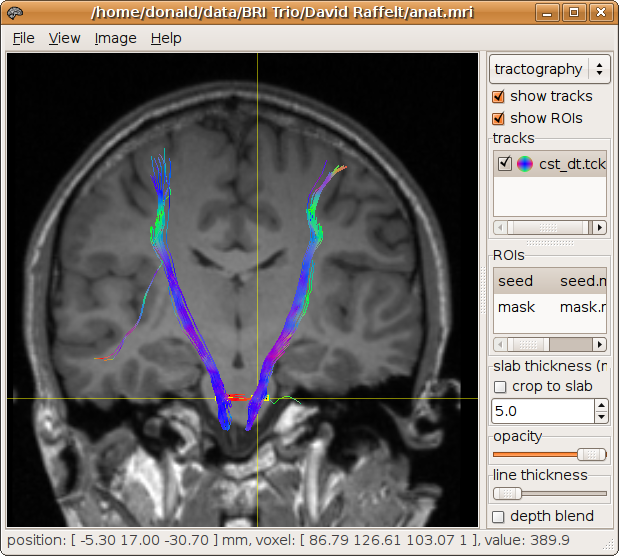
The results are displayed below (see here for more information on displaying results):

Multiple regions of interest can additionally be specified. For example, an inclusion region can be specified to discard tracks that do not pass through it:
> streamtrack DT_STREAM dwi.mif -seed -5.3,17,-30.7,4 -mask mask.mif cst_dt.tck -include -28,-14,53,30
173 generated, 100 selected [100%]

Alternatively, an exclusion region can be specified to discard tracks that do pass through it:
> streamtrack DT_STREAM dwi.mif -seed -5.3,17,-30.7,4 -mask mask.mif cst_dt.tck -exclude 27,16,21,20
124 generated, 100 selected [100%]

Any of these regions can also be specified as a mask image. The ROI analysis tool in MRView can be used to draw a specific ROI of interest, which can then be used for tracking (see here for details). For example, we generate a mask image called seed.mif, corresponding to both cortico-spinal tracts at the level of the pons:

It can be used as a ROI for tracking simply by specifying this image instead of the 4-component spherical ROI specification:
> streamtrack DT_STREAM dwi.mif -seed seed.mif -mask mask.mif cst_dt.tck
133 generated, 100 selected [100%]
To perform fibre-tracking using the orientations provided by constrained spherical deconvolution, simply change the first argument to the streamtrack command to SD_STREAM or SD_PROB, and supply the CSD SH coefficients file instead of the DWI image.
Specifying SD_STREAM as the tracking method will cause the program to use a deterministic fibre-tracking algorithm that simply follows the peaks of the fibre orientation distribution.
Specifying SD_PROB as the tracking method will cause the program to use a probabilistic fibre-tracking algorithm that uses orientations sampled from the fibre orientation distribution at each step (similar to e.g. Behrens et al., 2003 and Parker et al., 2003).
> streamtrack SD_PROB CSD8.mif -seed seed.mif -mask mask.mif cst_csd.tck
1121 generated, 1000 selected [100%]

Whole brain tracking can be performed for example by specifying the brain mask as both the seed and mask regions:
> streamtrack SD_PROB CSD8.mif -seed mask.mif -mask mask.mif whole_brain.tck -num 5000 7311 generated, 5000 selected [100%]

The results of whole-brain tracking can be used to generate high-resolution track-density images (Calamante et al. 2010):
> tracks2prob whole_brain.tck -vox 0.5 tdi.mif tracks2prob: creating new template image... - ok tracks2prob: mapping tracks to image... 100% tracks2prob: writing image... 100%
Note that to obtain good quality TDI maps, a very large number of tracks need to be generated (of the order of 1 million or more). See Calamante et al. 2010 for details. For other TDI options (e.g. DEC-TDI), see the help page for tracks2prob.

 |
 |
 |
top |  |
|---|